VAKIFBANK
ANNUAL REPORT 2014
27
Japan is also continuing to pursue expansionary policies to
stimulate its economy. The Bank of Japan (BoJ) declared
that it would continue its expansionary monetary policy
until the inflation rate reaches 2%. An increase in the
consumption tax in April negatively affected economic
activity. As the economy was already facing recession risk,
increasing taxes from 5% to 8% to shrink its budget deficit
played a major role in causing the economy to contract for
two consecutive quarters. As a result, the second phase of
the tax increase world’s has been postponed.
THE WORLD’S ECONOMIES HAVE CONTINUED
TO GRAPPLE WITH DEFLATION
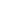
The economies of developing and developed countries
have continued to grapple with deflation risk in 2014.
In contrast with countries implementing expansionary
monetary policies, the US economy, which had already
begun to implement exit strategies in 2014, recorded
an inflation rate of 0.8% in 2014, falling below the 2%
inflation rate targeted by the Federal Reserve. In the
Eurozone, prices declined by 0.2% on an annual basis in
2014. While this situation raised concerns about deflation
in the economy, it revealed that the ECB needed to
introduce new measures as part of its expansionary
monetary policy. Despite the ongoing expansionary
policies in Japan, concerns about low inflation lingered in
2014. The IMF forecasts that inflation will rise in the US,
Eurozone, and China in 2015 while declining moderately
in Japan.
THE SHARP DROP IN OIL PRICES
Oil prices dropped dramatically during 2014. Exhibiting a
downward trend since June, oil prices started to fall from
US$110 per barrel and ended the year at US$ 53.7 per barrel.
An increase in oil supply and a downward revision in oil
demand forecasts in the coming years by international energy
institutions caused this precipitous decline in oil prices. The
decision of OPEC at its meeting on November 27 to leave
the level of production unchanged accelerated the decline in
oil prices. This had a positive effect on the economies of oil
importing countries such as Turkey, while negatively affecting
oil exporting countries such as Russia.
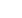
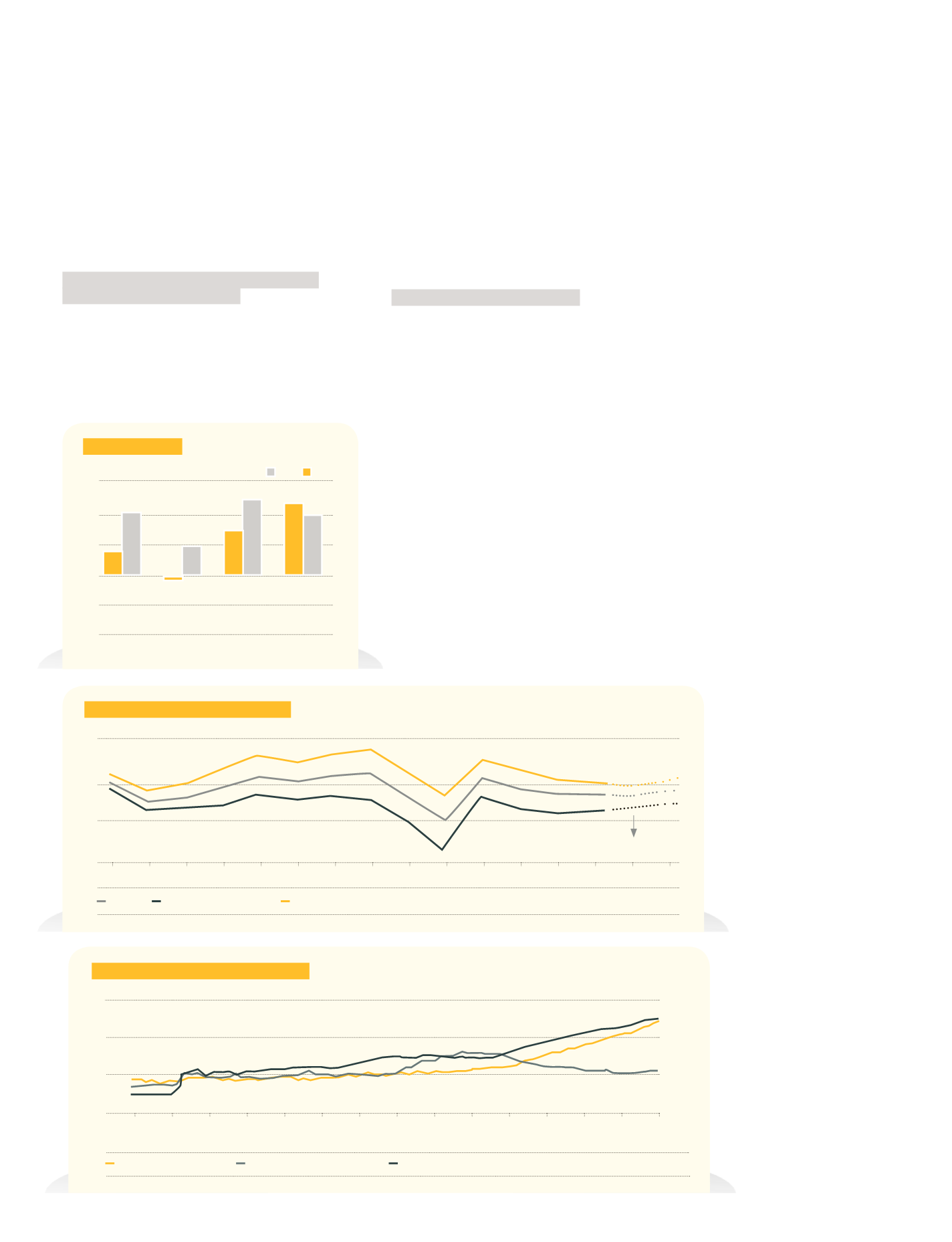
REAL ECONOMIC GROWTH
(Y-Y, %)
10
5
0
-5
Source: IMF
2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008
2010
2009
2011
2013 2014
2012
2015
World
Developed Countries
Developing Countries
Expectation
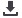
CENTRAL BANK BALANCE SHEET SIZE
01/08
07/08
01/09
07/09
01/10
07/10
01/11
07/11
01/12
07/12
01/13
07/13
01/14
07/14
01/15
US (billion dollar, left axis)
Euro Area (billion euro, left axis)
Japan (trillion yen, right axis)
6,000
400
300
200
100
4,000
2,000
0
0
Source: Bloomberg
INFLATION
(%)
US
Euro Area
Japan
China
2015
2014
3
2
1
-1
0
Source: IMF
*IMF Expectation
0.8
2.1
-0.2
1
1.5
2.5
2.4
2